

Choosing a cloud data warehouse: Comparing some of the top CDW vendors
There are many popular cloud-based data warehouse platforms to choose from, including Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, Microsoft Azure, Snowflake and others — and there are just as many important considerations when deciding on the right solution for your organization.
While many of the popular cloud data platforms offer similar capabilities, you’ll find many differences in pricing, scalability, architecture, security features, speed, and other factors.
Here we compare the four top vendors for the enterprise:
Amazon vs. Azure vs. Google vs. Snowflake
Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics: Taking SQL beyond data warehousing.
Azure Synapse Analytics is a newer analytics service that brings together enterprise data warehousing and big data analytics. It gives you the freedom to query data using either serverless on-demand or provisioned resources. Azure Synapse offers a unified experience to ingest, prepare, manage, and serve data for your business intelligence (BI) and machine learning (ML) needs.
At the heart of Azure Synapse is a cloud-native, distributed SQL processing engine. It’s built on the foundation of SQL Server to drive your most demanding enterprise data warehousing workloads. Similar to other cloud MPP solutions, Azure SQL Data Warehouse (SQL DW) separates storage and compute, billing for each separately. Azure Synapse saves relational tables data with columnar storage and abstracts physical machines by representing compute power in the form of data warehouse units (DWUs). This allows your users to easily and seamlessly scale compute resources at will.
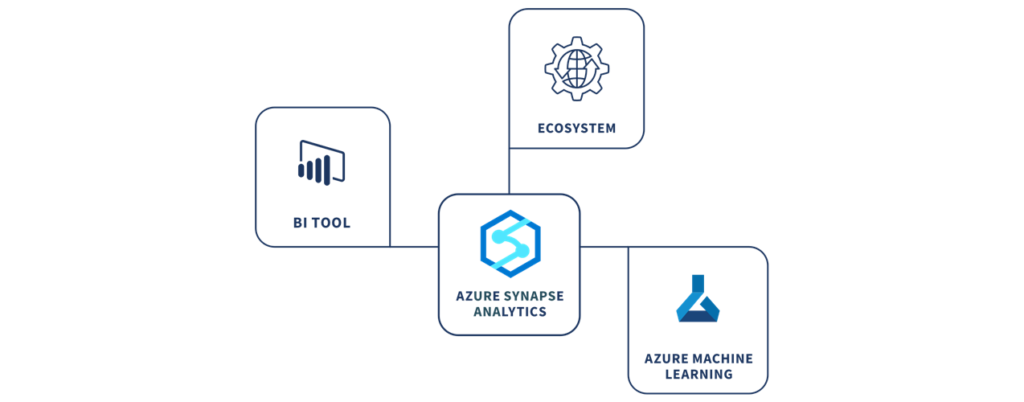

Synapse Analytics aims to unify a range of analytics workloads, such as data warehouses or data lakes, and ML, in a singular user interface (UI). The combination of an SQL Engine, Apache Spark with Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS), and Azure Data Factory gives users the option to control both data warehouse/data lakes and data preparation for ML tasks. Azure Synapse allows for both vertical and horizontal scaling of the data warehouse. Vertically by changing the service tier or placing the database in an elastic pool. Horizontally by adding more data warehouse units.
Google BigQuery: A serverless solution.
BigQuery is a fully managed, serverless data warehouse that automatically scales to match storage and computing power needs. Google doesn’t expect you to manage your data warehouse infrastructure which is why BigQuery hides many of the underlying hardware, database, nodes, and configuration details. Its elasticity automatically works out of the box. And getting started is simply a matter of creating an account with Google Cloud Platform (GCP), loading a table, and running a query. Google takes care of the rest.
With BigQuery, you get a columnar and ANSI SQL database that can analyze terabytes to petabytes of data at incredible speeds. BigQuery also lets you do spatial analysis using familiar SQL with BigQuery GIS. In addition, you can quickly build and operationalize ML models on large-scale structured or semi-structured data using simple SQL with BigQuery ML. And you can support real-time interactive dashboarding with BigQuery BI Engine.
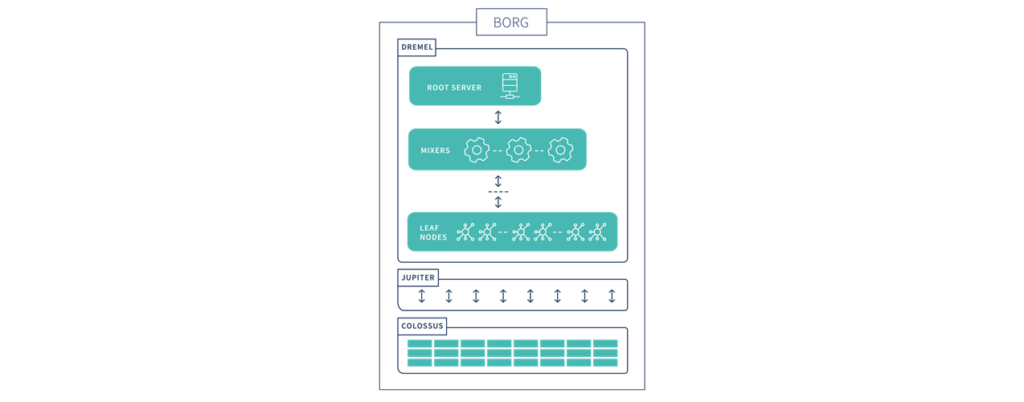

The BigQuery architecture is composed of several components. Borg is the compute. Colossus is the distributed storage. Jupiter is the network. And Dremel is the execution engine.
Amazon Redshift: The first widely adopted cloud data warehouse.
For many years, data warehousing was only available as an on-premise solution. Then in November 2012, Amazon Web Services (AWS) launched Redshift, a fully managed, petabyte-scale data warehouse service in the cloud. Although not the first cloud-based data warehouse, it was the first to gain market share through adoption. Redshift’s SQL dialect is based on PostgreSQL, which is well understood by analysts worldwide, and uses an architecture familiar to many on-premises data warehouses users.
You can start with as little as a few gigabytes of data and scale to petabytes. This empowers you to acquire new insights from your business and customer data.
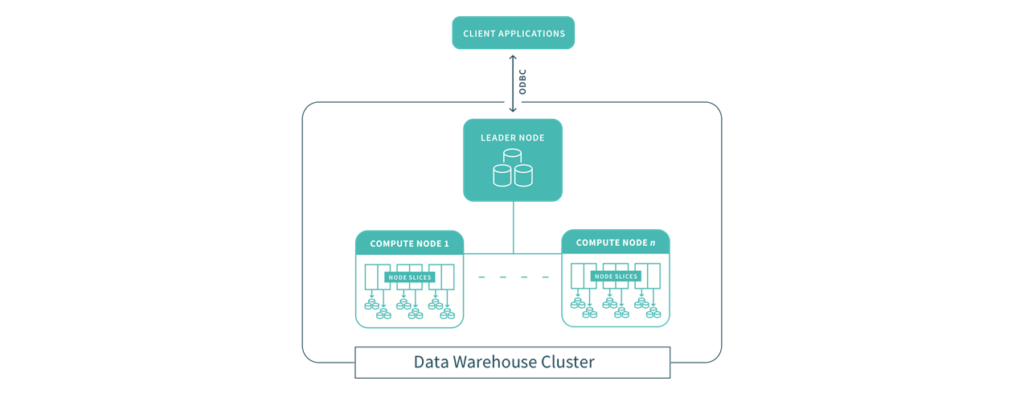

The first step to creating a Redshift data warehouse is to launch a set of nodes, called an Amazon Redshift cluster. After you provision your cluster, you upload your data set and then perform data analysis queries. Regardless of the size of your data set, Amazon Redshift delivers fast query performance using familiar SQL-based tools and business intelligence applications.
Snowflake Cloud Data Warehouse: The first multi-cloud data warehouse.
Snowflake is a fully managed MPP cloud-based data warehouse that runs on AWS, GCP, and Azure. Snowflake, unlike the other data warehouses profiled here, is the only solution that doesn’t run on its own cloud. With a common and interchangeable code base, Snowflake features global data replication, which means you can move your data to any cloud, in any region — without having to re-code your applications or learn new skills.
When you’re a Snowflake user, you can spin up as many virtual warehouses as you need to parallelize and isolate the performance of individual queries. Snowflake enables very high concurrency by separating storage and compute to ensure that many warehouses can simultaneously access the same data source.
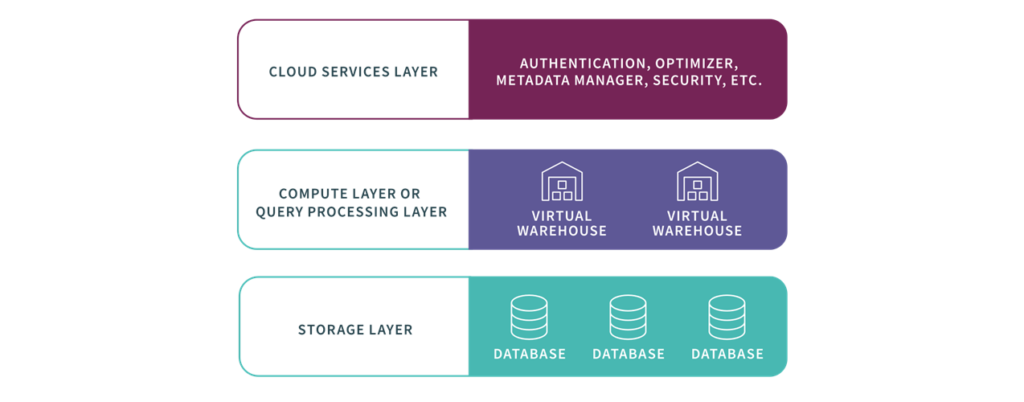

You interact with Snowflake’s data warehouse through a web browser, the command line, an analytics platform, or via Snowflake’s ODBC, JDBC, or other supported drivers. The platform supports ACID-compliant relational processing and has native support for document store formats such as JSON, Avro, ORC (Optimized Row Columnar), Parquet, and XML.
Taken directly from: https://www.qlik.com/us/cloud-data-migration/cloud-data-warehouse
We’re not recommending or suggesting any of these services. Innovoco can help you evaluate the different CDW options available and suggest the best fit for your needs. Learn more at Innovoco.com and book a free-consultation to evaluate your CDW needs.
Learn more about how Innovoco facilitates Cloud Data Warehouse projects by starting small and simple.
Pick a day here, we’ll send you a Skip the Dishes/Uber Eats EGift Card, and we can chat over Teams.
Sneak preview:
- We will NOT bore you with the commonly cited benefits of cloud data warehouses
- We will present 2 specific paths to move from Legacy Data Warehouses to the Cloud:
- MS Azure – recent developments in Synapse and Databricks that make it very easy to build a data warehouse by starting off small and building up.
- Google BigQuery – Google has been trying to steal market share by offering rock bottom pricing and interesting features.
Pick a day here.
